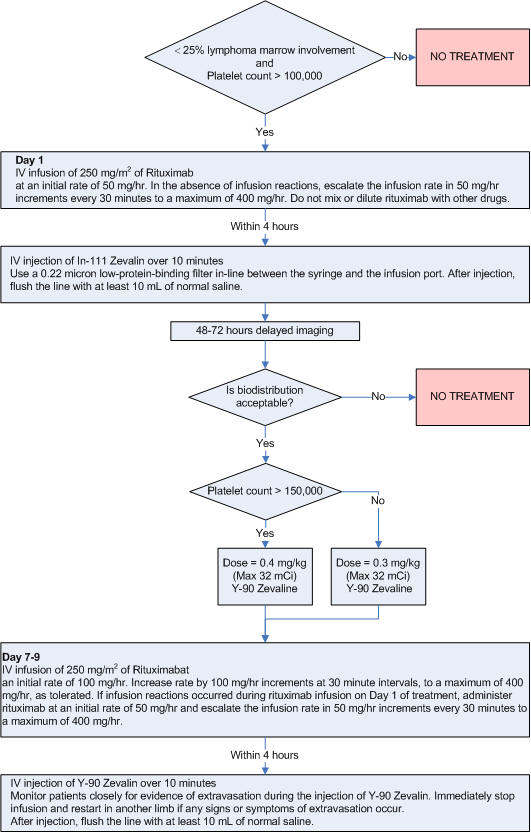

Expected Biodistribution:
• Activity in the blood pool areas (heart, abdomen, neck, and extremities)
may be faintly visible.
• Moderately high to high uptake in normal liver and spleen.
• Moderately low or very low uptake in normal kidneys, urinary bladder, and
normal (uninvolved) bowel.
• Non-fixed areas within the bowel lumen that change position with time; delayed
imaging may be necessary to confirm gastrointestinal clearance.
• Focal fixed areas of uptake in the bowel wall (localization to lymphoid
aggregates in bowel wall).
• Tumor uptake may be
visualized however tumor visualization on the In-111 Zevalin scan is not
required for Y-90 Zevalin therapy.
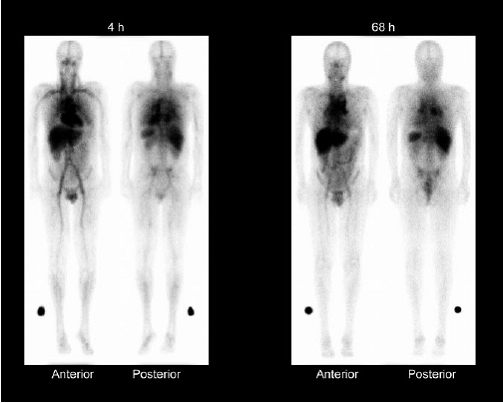
Whole-body g-camera images obtained at 4 and 68 h after administration of 111In-ibritumomab tiuxetan, showing expected biodistribution, with the radiopharmaceutical easily detectable in the blood-pool areas on 4-h images. Moderately high or high uptake in normal liver and spleen is seen on 4- and 68-h images, and moderately low or very low uptake in normal kidneys, urinary bladder, and bowel is seen on 4- and 68-h images. Tumor uptake is seen in mediastinal lymph nodes.
Altered Biodistribution
The criteria for altered biodistribution are met if any of the following is
detected on visual inspection of the required gamma images:
• Intense localization of radiotracer in the liver and spleen and bone marrow
indicative of reticuloendothelial system uptake.
• Increased uptake in normal organs (not involved by tumor) such as:
o Diffuse uptake in normal lung more intense than the liver.
o Kidneys have greater intensity than the liver on the posterior view.
o Fixed areas (unchanged with time) of uptake in the normal bowel greater than
uptake in the liver.
o In less than 0.5% of patients receiving In-111 Zevalin, prominent bone marrow
uptake was observed, characterized by clear visualization of the long bones and
ribs. Consider bone marrow involvement by lymphoma, increased marrow activity
due to recent hematopoietic growth factor administration, and increased
reticuloendothelial uptake in patients with HAMA and HACA, as possible causes of
prominent bone marrow uptake. Re-assess biodistribution after correction of
underlying factors.
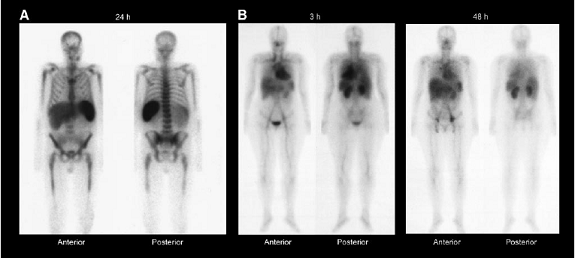
Whole-body g-camera images of representative patients obtained at 24 h after administration of 111In-ibritumomab
tiuxetan (A), showing prominent bone marrow and splenic uptake, and at 3 and 48 h after administration of 111In-ibritumomab tiuxetan (B), showing greater than expected renal uptake.